Our Services
What does medical oncologist mean?
The word “Oncologist” refers to doctors with specialized expertise in the treatment of cancer. As cancer specialists, we are your partners and friends in the battle against cancer. Medical Oncologists are doctors who specialize in the systemic therapy of cancer. We try to ensure that cancer is either permanently cured or controlled for as long as possible using treatments that have maximum benefit with minimum side-effects. Commonly used treatments in medical oncology include chemotherapy, targeted therapy, hormone therapy, and immunotherapy. You can learn more about these therapies by using various sections of this website.
Major Departments involved in a cancer care
Comprehensive Cancer care involves all the 3 departments and none of the department is disposable. A proper discussion between all 3 is required to plan a treatment for the patient and after planning depending on the treatment required the respective department takes care of the patient.For example if chemotherapy is required then a medical oncologist is required. Similarly if patient requires surgery a surgical oncologist is required
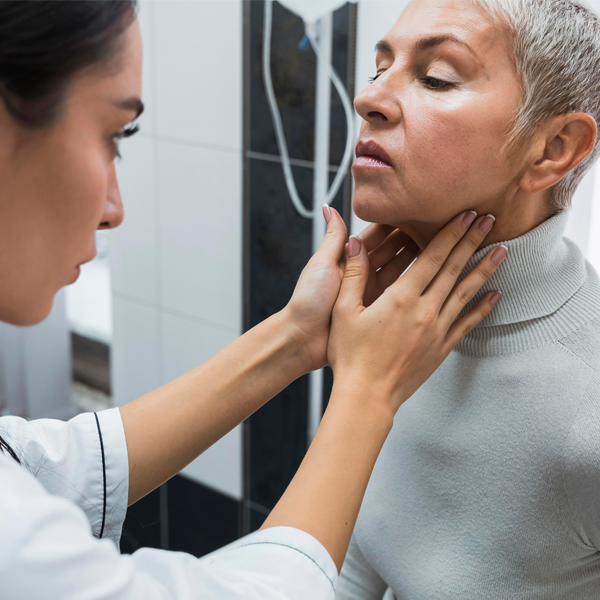
Head and neck cancer
Head and neck cancer comprises malignancies in the squamous cells of the mouth, throat, larynx, sinuses, and nasal cavity. Major risk factors include tobacco, alcohol, and HPV infection. Symptoms vary but can include a persistent sore throat, difficulty swallowing, and changes in voice.
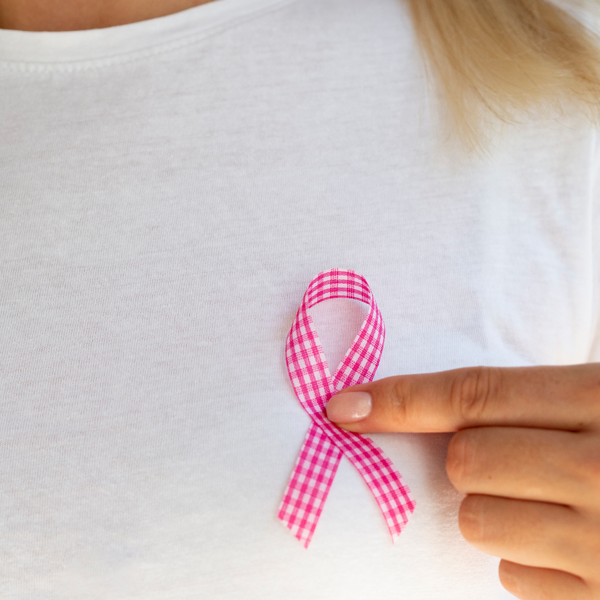

Breast Cancer
Breast cancer originates in the cells of the breast, often in the ducts or lobules. Key risk factors include genetics, age, and lifestyle, with symptoms like a lump in the breast, changes in shape, or nipple discharge. Early detection through mammograms significantly improves treatment outcomes.
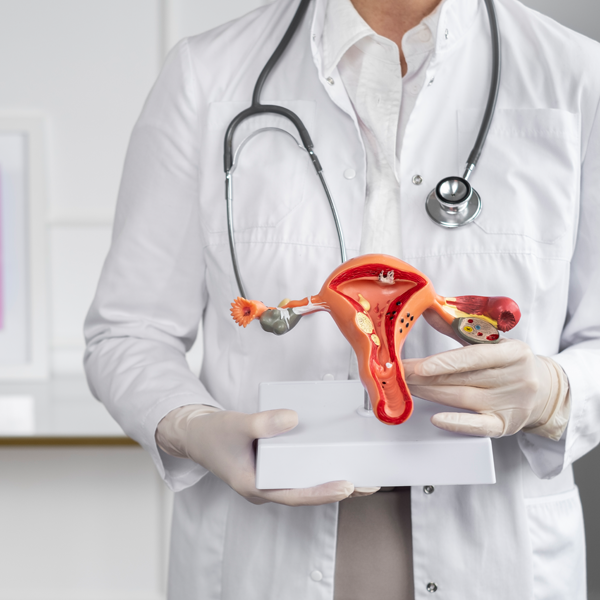
Ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer begins in the ovaries and is often detected at an advanced stage due to subtle symptoms like bloating, pelvic pain, and frequent urination. Risk factors include age, genetics, and family history. Early detection is challenging but critical for effective treatment.

Hepatopancreatic Cancer
Hepatopancreatic cancer involves malignancies in the liver and pancreas, often presenting with late-stage symptoms such as jaundice, abdominal pain, and weight loss. Major risk factors include chronic liver disease, smoking, and family history. Early detection is difficult, making prognosis generally poor.
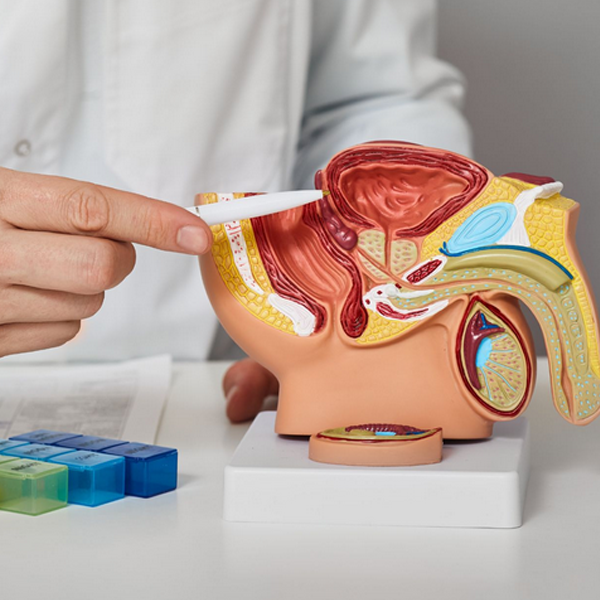
Prostate cancer
Prostate cancer develops in the prostate gland, often growing slowly and initially presenting few symptoms. Risk factors include age, family history, and genetics, with symptoms like difficulty urinating and pelvic discomfort. Early detection through PSA testing can improve treatment outcomes.
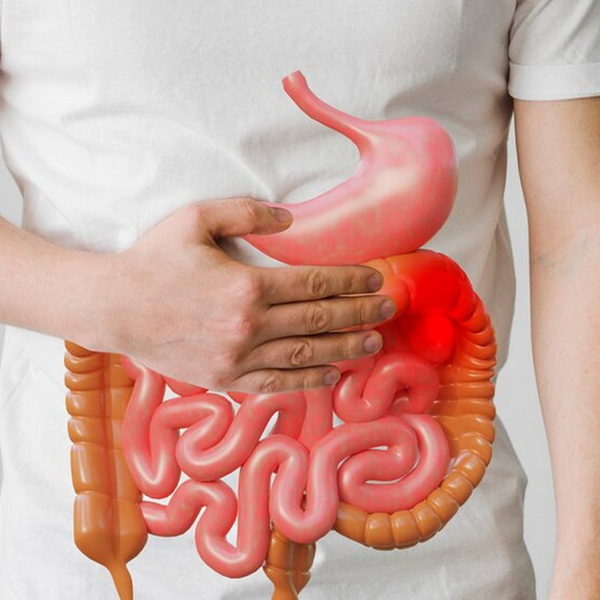
Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancer originates in the colon or rectum, with symptoms such as changes in bowel habits, blood in the stool, and abdominal discomfort. Risk factors include age, diet, and family history. Early detection through screening like colonoscopy significantly enhances treatment success.
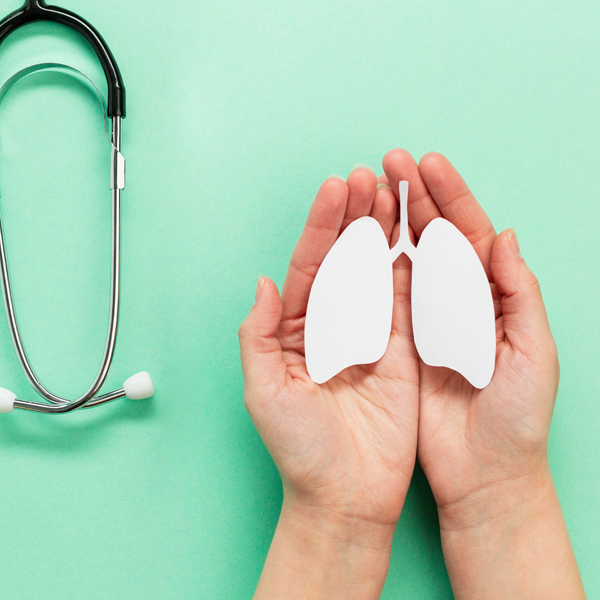

Lung Cancer
Lung cancer starts in the lungs, often caused by smoking, with symptoms like persistent cough, chest pain, and shortness of breath. Major risk factors include smoking, exposure to radon, and family history. Early detection through imaging and screening can improve treatment outcomes.
Endometrial Cancer
Endometrial cancer begins in the lining of the uterus (endometrium), typically presenting with abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, or changes in menstrual patterns. Risk factors include obesity, hormonal imbalances, and age. Early diagnosis and treatment offer better chances of successful outcomes.


